Rail Testing Equipment: Types, Technologies and Features
Rail Flaw Detectors: Ultrasonic and Eddy Current Testing Methods
Portable Flaw Detectors for Manual Rail Testing
Hand-Pushed Trolleys for Rail and Welded Joint Testing
High-Speed Railway Systems for Rail Crack Detection
For the railroad industry, it is crucial that rails and welded joints remain durable and reliable. Cracks and other defects can compromise their strength, resulting in broken rails, damaged trains, and accidents. Long-term operation increases the risk of critical rail defects, including those caused by rolling contact fatigue. Therefore, regularly inspecting the rails and welds is essential for enabling timely repairs or replacements and ensuring the safety of rail traffic.
Rail flaw detectors are engineered to identify defects in rails and welded joints, including those that are invisible to the naked eye or in the early stages of development. These devices use ultrasonic (UT) and eddy current (ET) technologies to provide nondestructive testing (NDT) specialists with accurate, real-time diagnostic data.
OKOndt GROUP develops, manufactures, and supplies a wide range of ultrasonic and eddy current rail inspection equipment. This includes single- and dual-rail flaw detector models for manual, continuous, and high-speed testing of rails and welds.
Ultrasonic flaw detectors:
Eddy current flaw detectors:
Rail Flaw Detectors for Ultrasonic and Eddy Current Testing
A dedicated rail flaw detector is required for each method—ultrasonic or eddy current—and is designed to detect the types of defects specific to that testing technique.
Ultrasonic Rail Testing
Ultrasonic testing can detect the presence, type, dimensions, and precise location of internal discontinuities, cracks, and other defects within the rail profile. This method uses high-frequency ultrasonic waves, typically ranging from 2 to 5 megahertz (MHz), for this purpose.
Defects in rails can vary in origin and characteristics. They may result from manufacturing flaws or operational stresses and differ in terms of their dimensions, location, depth, and crack development direction. To detect and accurately determine these parameters, ultrasonic waves are introduced into the rail at multiple angles, typically from two to four. For this purpose, flaw detectors are equipped with various testing schemes that employ ultrasonic probes of different configurations. Each probe emits ultrasound beams at a specific angle in relation to the rail surface to target particular areas within the rail head, web, and base. Together, these probes ensure a thorough inspection of the entire rail profile, excluding the foot flanges.
Various ultrasonic testing methods and techniques are used in rail flaw detectors, primarily the pulse-echo and echo-shadow methods. Furthermore, ultrasonic rail testing equipment utilizes an echo-image technique that displays probe data in real time on the detector screen in various formats, including A-scan, B-scan, and combinations of the two. The built-in software of the rail flaw detector provides this visualization. It gives NDT specialists clear, comprehensive information about rail testing results.
Surface and near-surface defects of the railhead, such as headchecks, delaminations, and squats, may develop during rail operation. These rolling contact fatigue rail defects initially appear on the surface of the rail and then gradually spread deeper into the rail over time. To extend the service life of the rails, these defects must be detected early and corrected with grinding machines.
Eddy current rail flaw (crack) detectors are used to detect these defects. These devices create an alternating magnetic field that induces eddy currents in the metal rail. If there are surface or near-surface defects on the railhead, the flow of eddy currents is disrupted. The eddy current crack detector records and analyzes these changes, enabling it to determine the presence and location of the defect.
Compared to ultrasonic testing, eddy current rail inspection is more sensitive to shallow surface cracks, making it especially effective at the early detection of railhead defects.
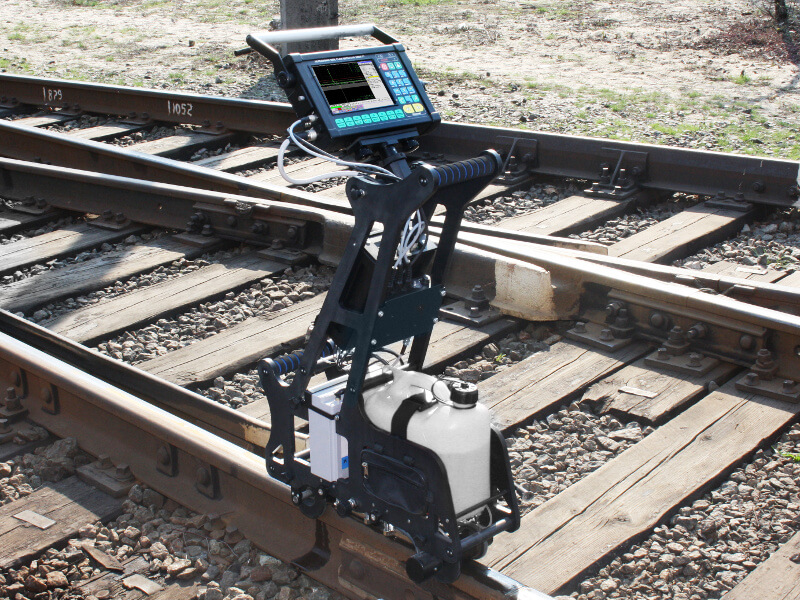
Portable Flaw Detectors for Manual Rail Testing
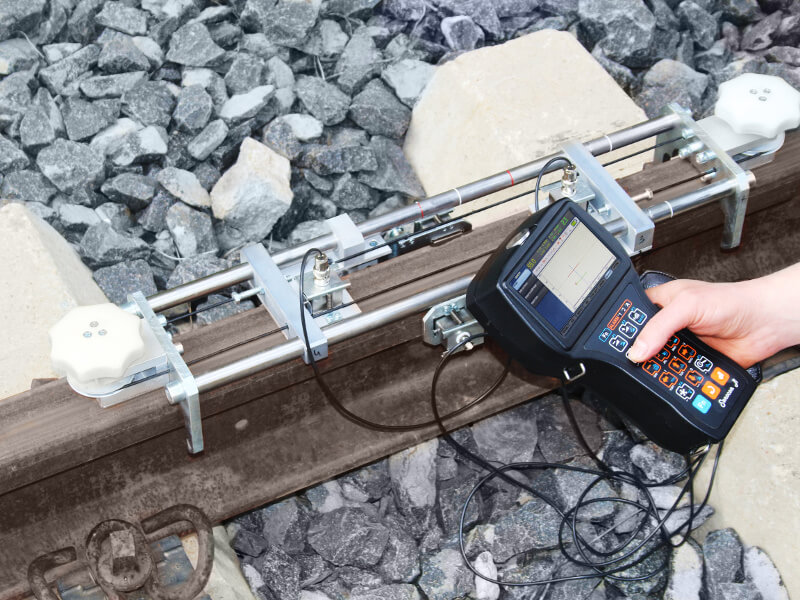

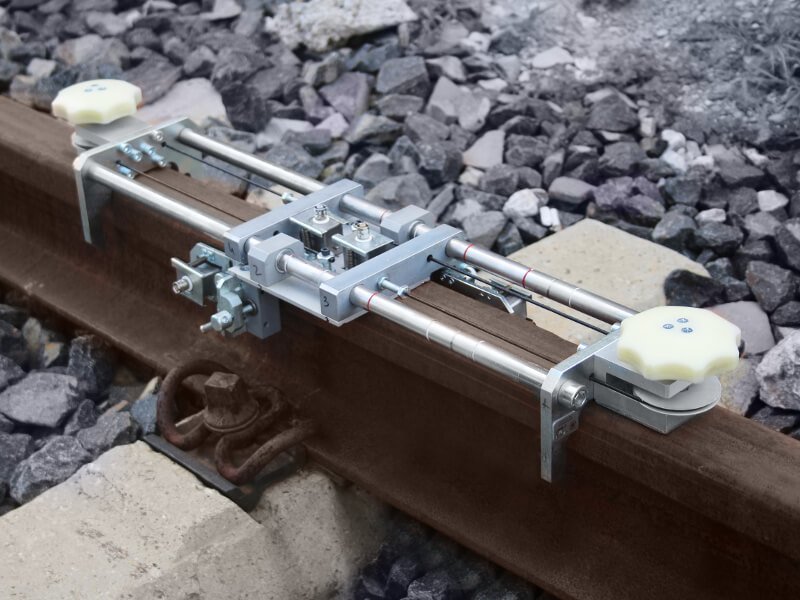
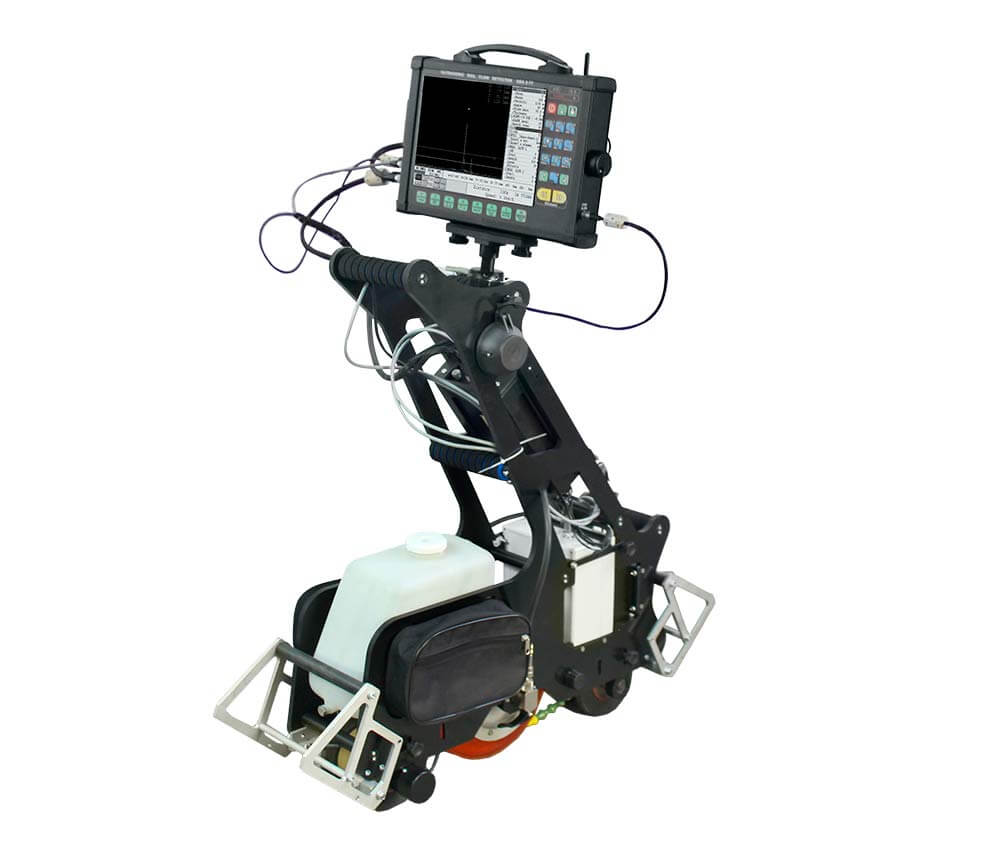
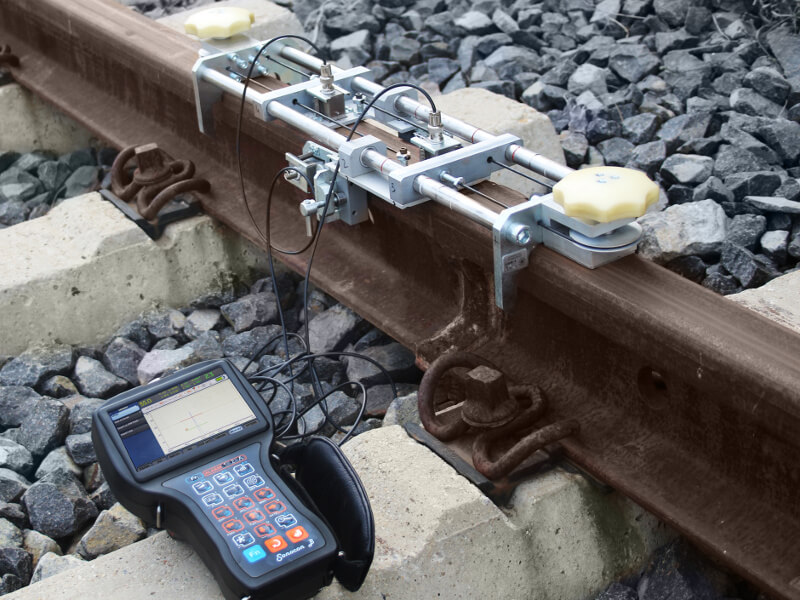
During the secondary (confirmatory) rail track inspection, which follows the initial inspection by high-speed Systems and hand-pushed carts, portable ultrasonic (UT) flaw detectors are used. Examples include the Sonocon B and Sonocon BL, which has a larger screen. These devices accurately detect and measure the type, depth, shape, and direction of development of defects in rails and welds. They are lightweight and user-friendly with a wide range of features, including precise measurement of the thickness of different materials, not only metal.
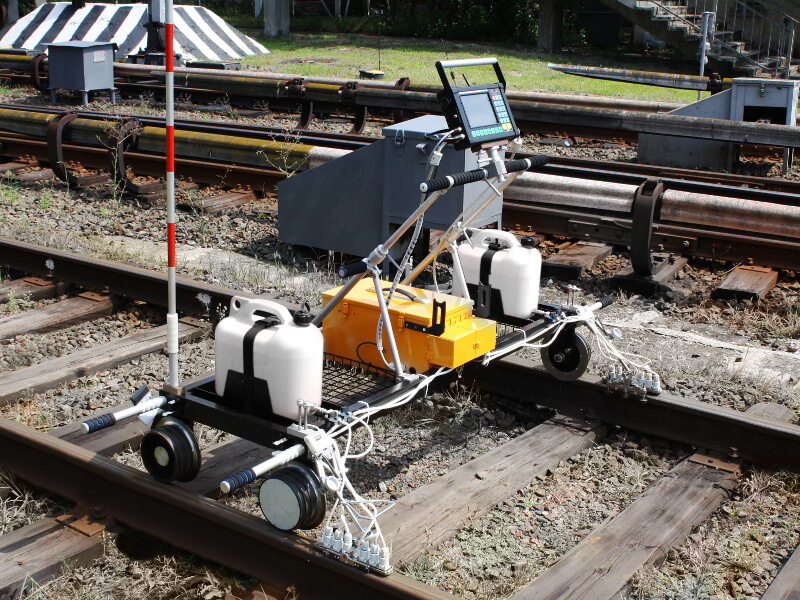
The USR-01 Set is used to inspect welded joints on railway tracks and to assess the ends of new and old rails before welding them at rail welding plants or directly at the track-laying site. The USR-01 unit includes a USR-01 rail scanner, a set of manual UT probes, and a Sonocon B portable flaw detector.
The Sonocon B enables manual scanning of rail-welded joints from the running and lateral surfaces of the rail. This method uses various probes (straight and angled) to provide a thorough evaluation of the rail head and web.
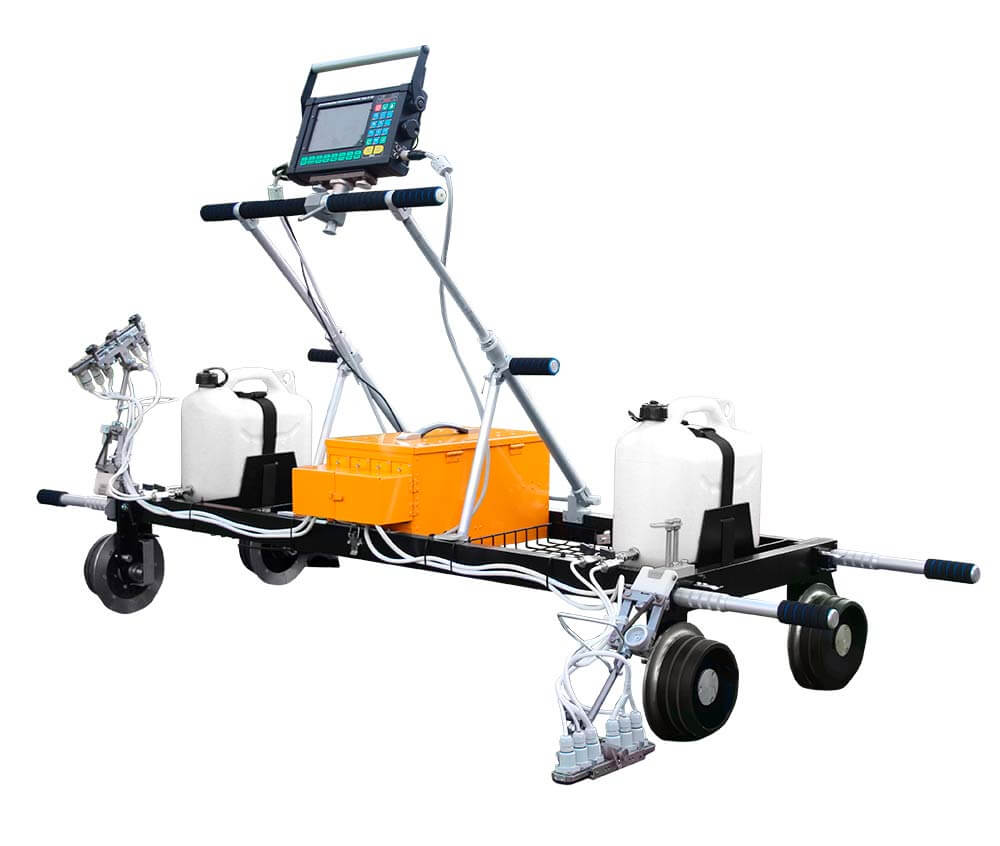
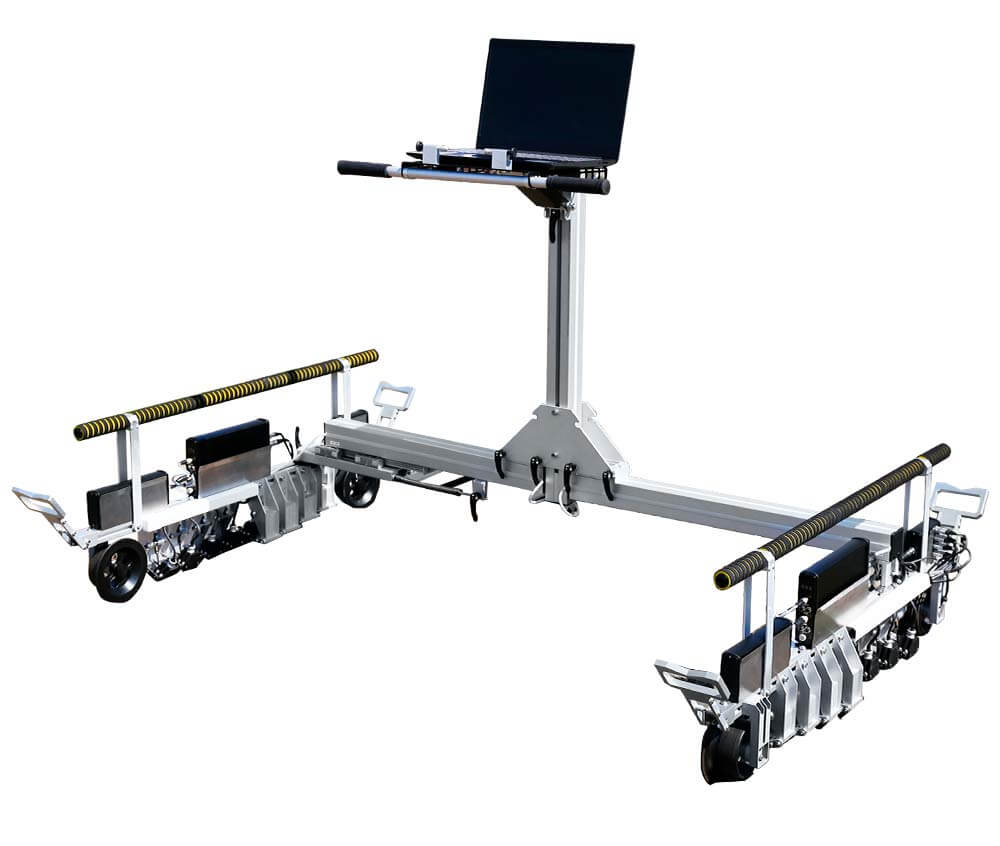
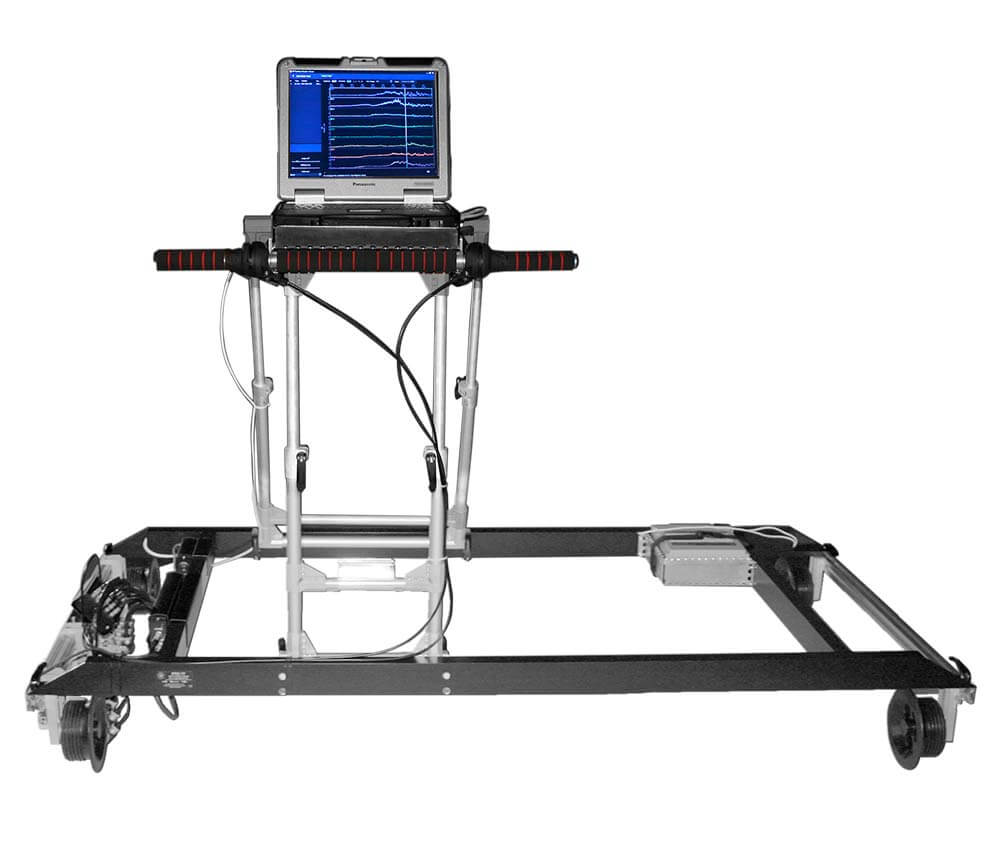
Hand-Pushed Trolleys for Rail and Welded Joint Testing
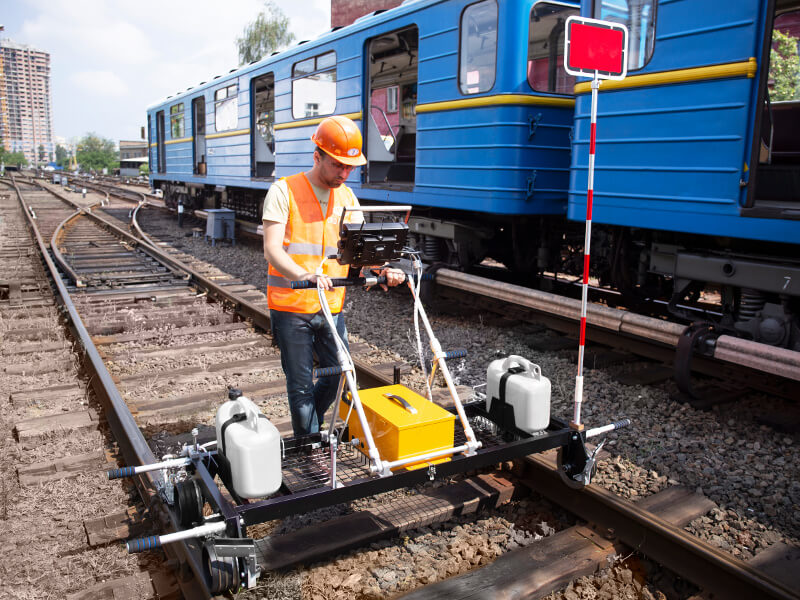
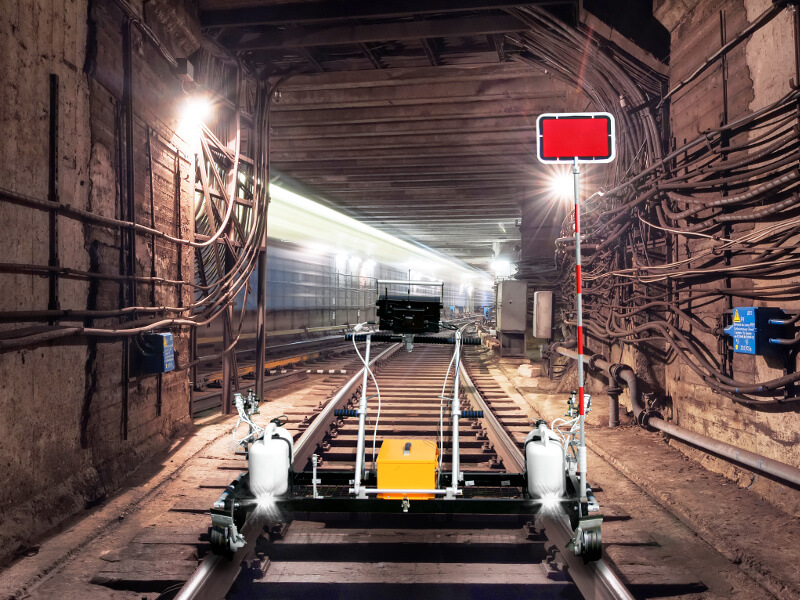
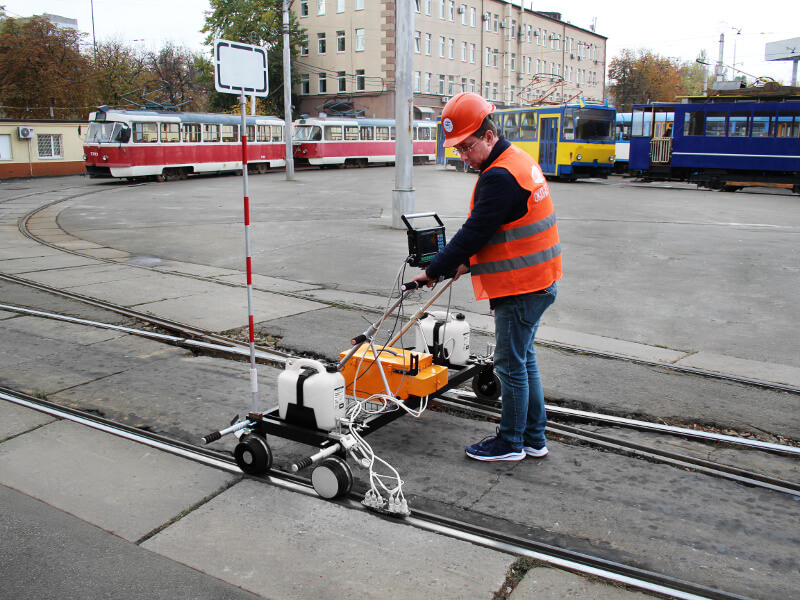
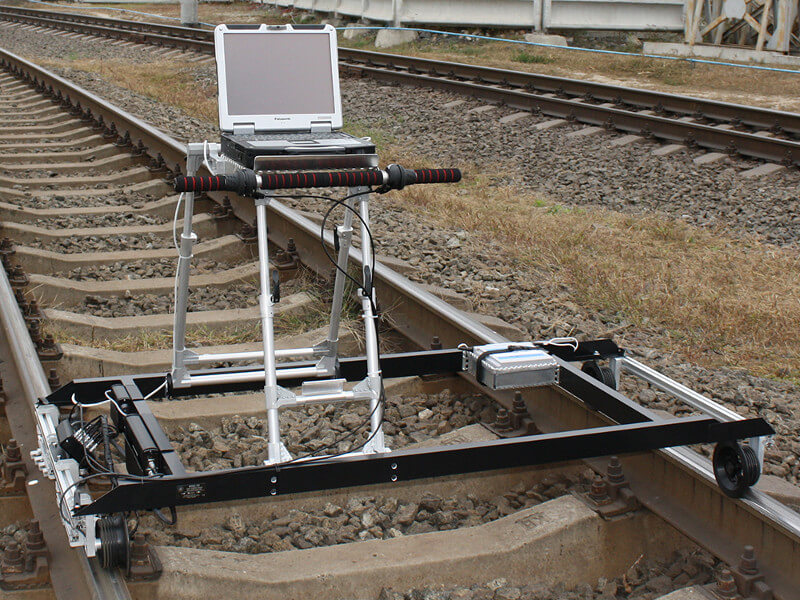
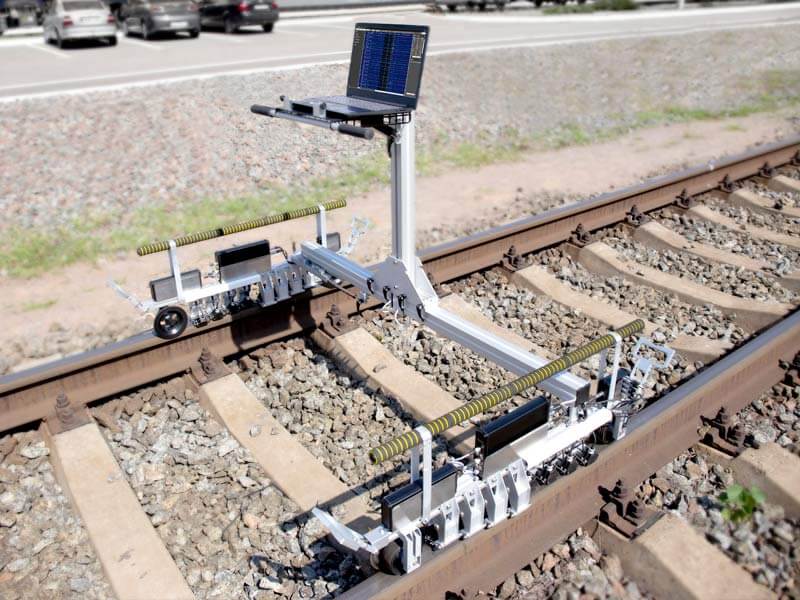





For NDT inspection of rails on short or complex railroad sections, as well as for confirmation of defects detected by high-speed rail testing Systems (based on hi-rail vehicles or cars), hand-pushed rail testing trolleys are used:
- Single-rail:
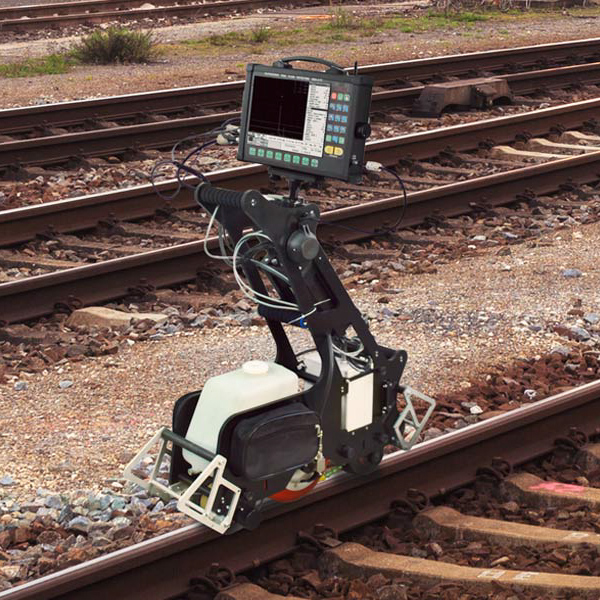
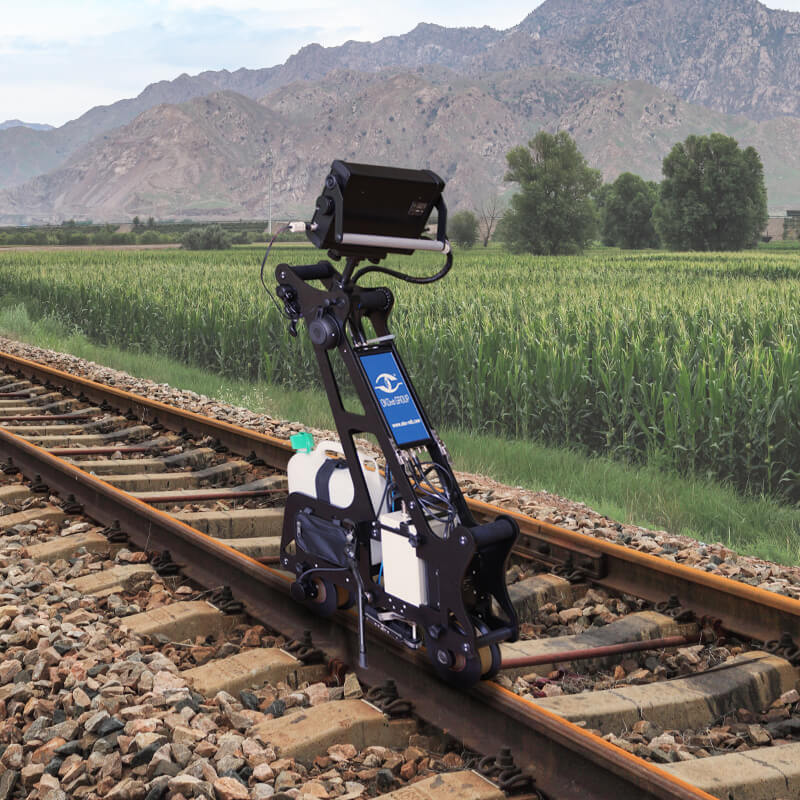
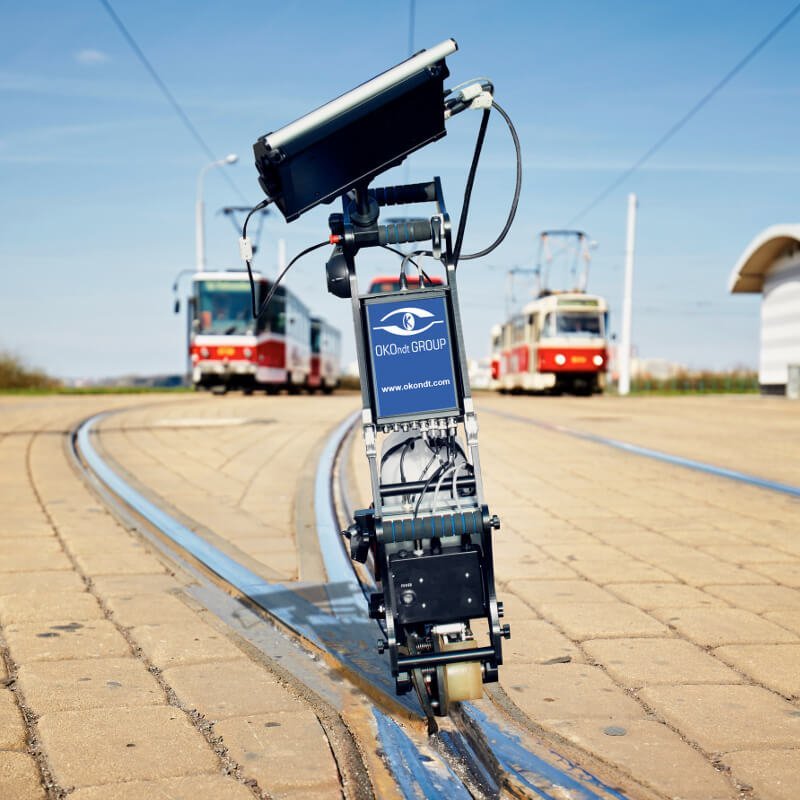
The single-rail flaw detector is lightweight, allowing NDT technicians to quickly place or remove it from the railway track when a train approaches. These trolleys are ideal for urgent rail testing and can scan narrow-gauge lines, sharp curves, and areas with obstacles, where the mobility of rail scanning equipment is essential.
- Double-rail:
Double-rail trolleys can monitor both rails of a track simultaneously. They are well-suited for routine, scheduled inspections of long, straight sections of railway.
Both the ultrasonic and the eddy current crack detectors have intuitive interfaces, automatic defect alarms, and flexible configurations with interchangeable probes and scanners. They have streamlined calibration using reference blocks. Ultrasonic carts can also be equipped with UT probe units designed as sliding blocks or wheels.
During the rail inspection process, the NDT technician can save data from the flaw detector to a flash drive and transmit it to the railway company. The company then takes the necessary steps to address the detected defects.



High-Speed Railway Systems for Rail Crack Detection
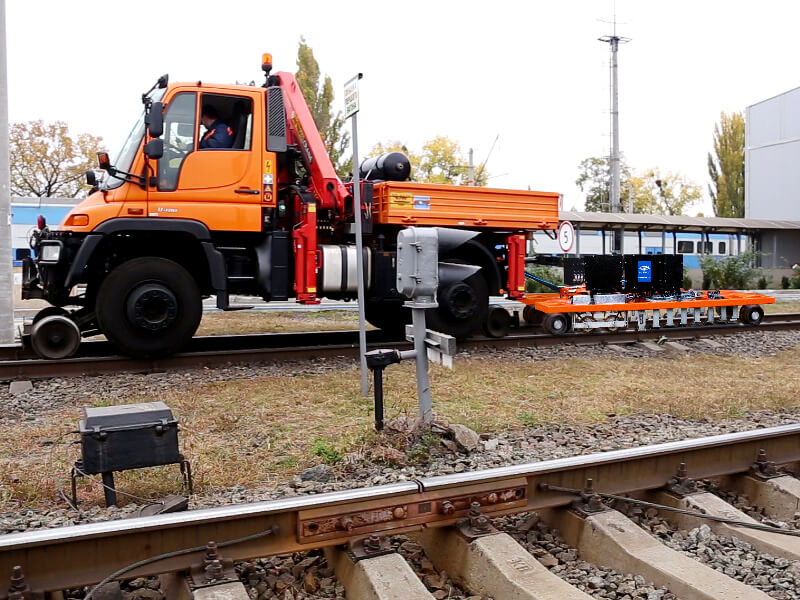
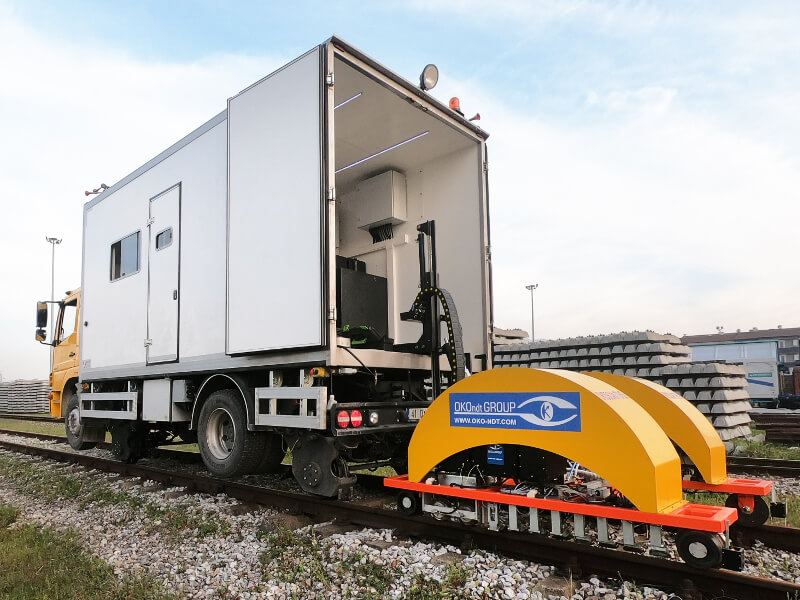
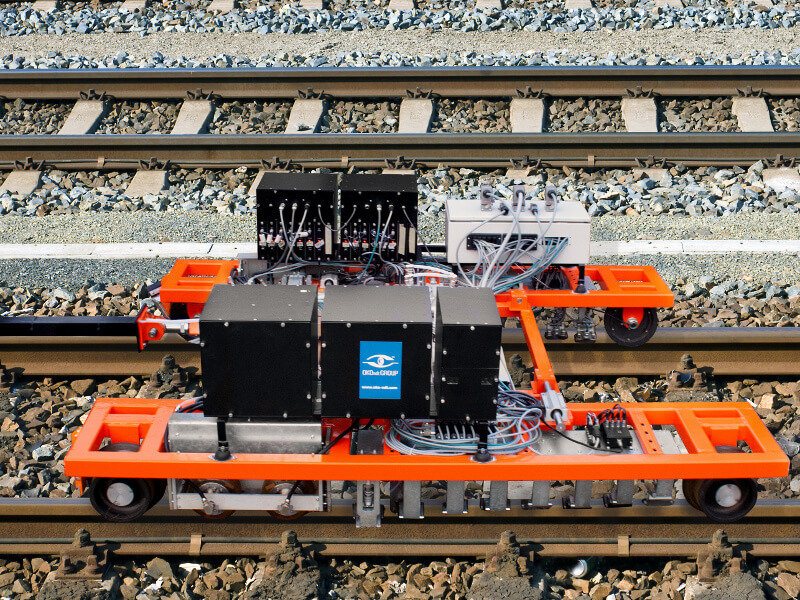



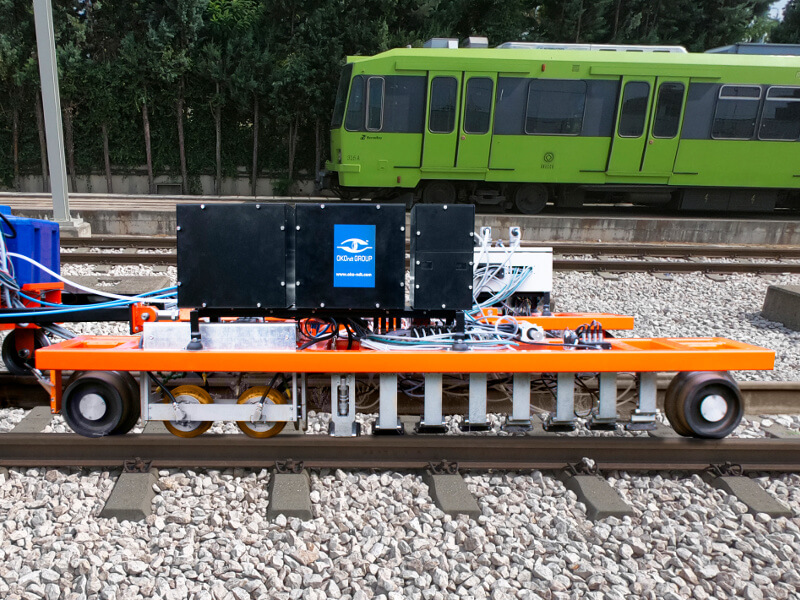
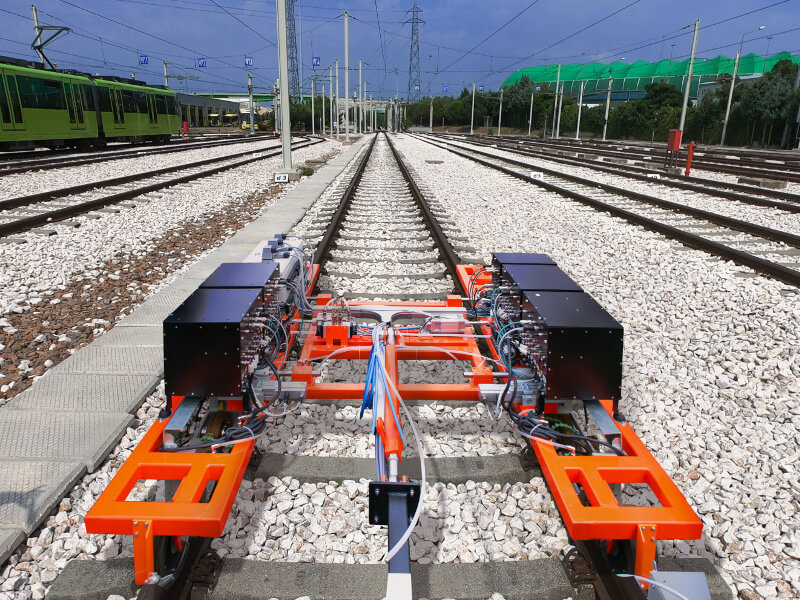
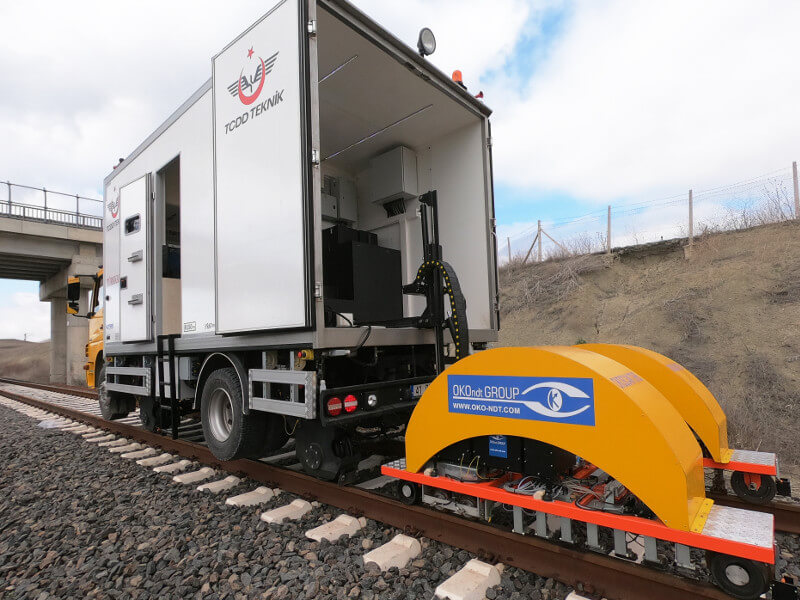
Long railway routes require automated NDT Systems for track inspections. The OKOSCAN UT 73HS, a high-speed rail testing System manufactured by OKOndt GROUP, is one such solution on the NDT market. This equipment can detect cracks in rails continuously at speeds of up to 25 mph (40 km/h), all while maintaining the geolocation of each defect. This allows NDT inspections to be performed with minimal disruption to train schedules.
The OKOSCAN UT 73HS includes a rail flaw detection trolley integrated with a hi-rail vehicle, search wheels with ultrasonic probes, ultrasonic modules, and dedicated software. The design of the System also allows the installation of an eddy current crack detector on the trolley.
OKOSCAN UT 73HS detects all types of critical rail defects at different stages of development and complies with AREMA, EN 16729-1, and UIC 712-R standards.










